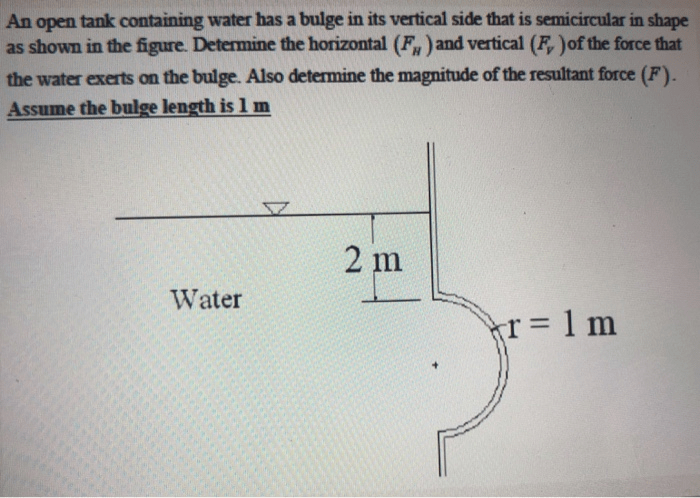
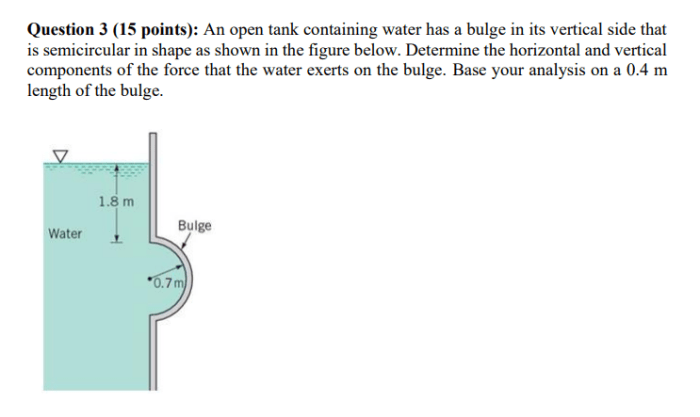
An open tank containing water has a bulge, a phenomenon that presents unique challenges and requires careful analysis to ensure structural integrity. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of tank bulges, exploring their causes, consequences, and effective mitigation strategies.
The bulge in an open tank containing water can induce stress concentrations within the tank’s walls, potentially leading to catastrophic failure if left unaddressed. Understanding the fluid-structure interaction and material properties involved is crucial for devising appropriate design considerations, inspection protocols, and repair techniques.
Structural Analysis: An Open Tank Containing Water Has A Bulge
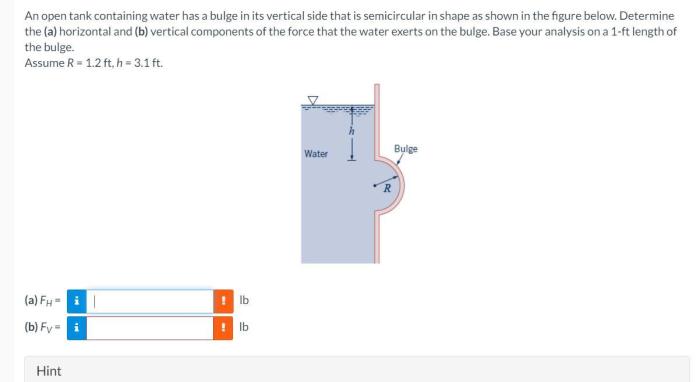
An open tank containing water has a bulge, which causes a non-uniform distribution of stress within the tank’s walls. The bulge introduces a concentration of stress at its apex, leading to increased risk of failure. The potential failure modes include:
- Plastic deformation: The bulge can cause the tank walls to deform plastically, resulting in permanent damage and loss of structural integrity.
- Buckling: The bulge can cause the tank walls to buckle, leading to catastrophic failure and the release of the contained fluid.
- Fracture: The bulge can initiate cracks in the tank walls, which can propagate and lead to catastrophic failure.
To prevent failure, it is crucial to identify the critical areas of the tank that require reinforcement. These areas are typically located at the apex of the bulge and along the lines of maximum stress concentration.
Fluid-Structure Interaction, An open tank containing water has a bulge
The bulge in the tank wall alters the fluid flow patterns within the tank. The bulge creates a local disturbance in the flow, which can lead to the formation of vortices and eddies. These vortices can exert additional hydrodynamic forces on the bulge, further increasing the stress concentration and risk of failure.
Additionally, the bulge can cause the tank to vibrate at its natural frequencies. This vibration can lead to resonance, which can amplify the hydrodynamic forces acting on the bulge and further compromise the tank’s integrity.
Material Properties
The material properties of the tank walls play a significant role in the behavior of the bulge. The yield strength, tensile strength, and fatigue resistance of the material determine its ability to withstand the stress concentrations and hydrodynamic forces caused by the bulge.
Corrosion, fatigue, and other environmental factors can degrade the material properties of the tank walls, making them more susceptible to failure. It is essential to select materials that are resistant to these factors and to implement proper maintenance practices to mitigate their effects.
Question Bank
What are the potential failure modes associated with a tank bulge?
Tank bulges can lead to various failure modes, including buckling, rupture, and collapse, compromising the tank’s integrity and posing safety hazards.
How does the material of the tank walls influence bulge behavior?
The material properties, such as strength, elasticity, and corrosion resistance, significantly impact the bulge’s formation and growth, affecting the tank’s overall structural stability.
What design modifications can be implemented to enhance a tank’s resistance to bulging?
Reinforcements, thicker walls, and optimized geometry can effectively mitigate bulge formation by distributing stresses more evenly and increasing the tank’s load-bearing capacity.