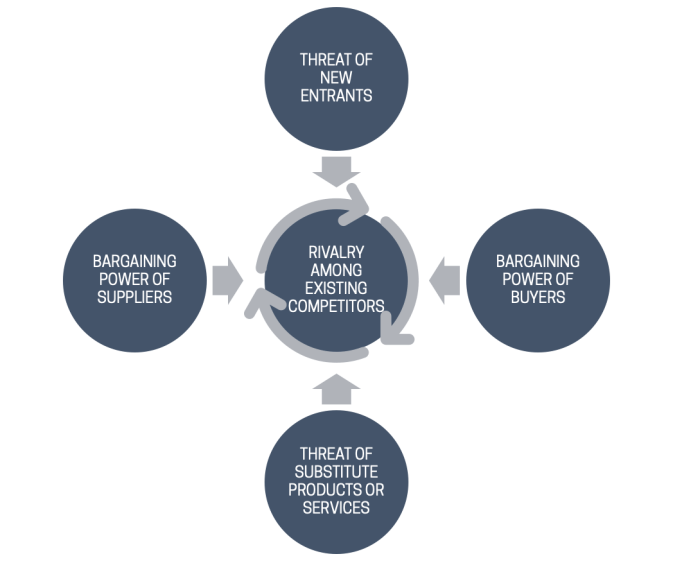
Porter’s five forces analysis airline industry – Porter’s Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating the competitive landscape of the airline industry. This analysis examines the intensity of competition, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes, offering valuable insights into the industry’s dynamics and potential challenges.
The airline industry is characterized by intense competition, with major players vying for market share and brand loyalty. Factors such as cost structure and operational efficiency play a crucial role in determining competitive advantage.
Industry Rivalry: Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Airline Industry
The airline industry is highly competitive, characterized by intense rivalry among major players. Market share, brand loyalty, and cost structure are crucial factors influencing the competitive landscape. Major airlines often engage in aggressive pricing strategies, frequent flyer programs, and differentiated service offerings to attract and retain customers.
Competitive Strategies
- Price wars and discounts to gain market share
- Loyalty programs and frequent flyer benefits to build customer loyalty
- Focus on cost efficiency and operational optimization to reduce operating expenses
- Expansion into new markets and routes to increase revenue streams
- Strategic alliances and partnerships to expand reach and reduce competition
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Key suppliers to the airline industry include aircraft manufacturers, fuel providers, and maintenance and repair service providers. Their concentration and ability to influence prices can significantly impact airlines’ profitability. Aircraft manufacturers, such as Boeing and Airbus, have a strong bargaining position due to their limited number and high switching costs for airlines.
Mitigation Strategies
- Long-term contracts and strategic partnerships to secure favorable pricing and supply assurance
- Diversification of supplier base to reduce dependency on a single provider
- Investment in fuel hedging strategies to mitigate fuel price volatility
- In-house maintenance and repair capabilities to reduce reliance on external suppliers
Bargaining Power of Buyers

Airline customers are highly price-sensitive and have a low switching cost, as they can easily choose alternative airlines or modes of transportation. This gives buyers significant bargaining power, especially during economic downturns or when there is excess capacity in the market.
Strengthening Position, Porter’s five forces analysis airline industry
- Offering flexible pricing and loyalty programs to attract and retain customers
- Providing differentiated services, such as premium seating, in-flight entertainment, and baggage handling, to enhance customer value
- Investing in technology and innovation to improve customer experience and reduce costs
- Building strong brand loyalty and reputation to increase customer preference
Threat of New Entrants
Barriers to entry in the airline industry are relatively high due to government regulations, capital requirements, and established networks of major airlines. New entrants face significant challenges in obtaining operating licenses, acquiring aircraft, and building a customer base.
Deterrence Strategies
- Maintaining high capital requirements and economies of scale to deter new entrants
- Engaging in strategic alliances and code-sharing agreements to strengthen market position
- Lobbying for government regulations that favor incumbents
- Offering exclusive benefits and loyalty programs to existing customers
Threat of Substitutes
Potential substitutes for air travel include high-speed rail, video conferencing, and private jets. While these alternatives may not fully replace air travel, they can pose a threat to certain segments of the market, such as short-haul flights or business travel.
Differentiation Strategies
- Focusing on unique value propositions, such as speed, convenience, and global reach
- Offering specialized services, such as cargo transportation or medical evacuation flights
- Investing in technology and innovation to improve customer experience and efficiency
- Collaborating with other travel providers to create seamless travel experiences
FAQ Insights
What is Porter’s Five Forces Analysis?
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis is a framework developed by Michael Porter to analyze the competitive environment of an industry.
How can Porter’s Five Forces Analysis be applied to the airline industry?
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis can be used to assess the competitive landscape of the airline industry, identifying factors that influence profitability and industry dynamics.