A nurse is assessing a client who has macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss among older adults. This comprehensive assessment involves evaluating visual acuity, visual fields, and other parameters to determine the impact of the condition on the client’s daily activities and overall well-being.
Macular degeneration affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. As the disease progresses, clients may experience blurred vision, distorted images, and difficulty recognizing faces and objects. These visual impairments can significantly impact their ability to perform daily tasks, navigate their environment, and maintain social connections.
Client Assessment
Assessing a client with macular degeneration is crucial to determine the extent of vision loss, identify areas of preserved vision, and develop appropriate interventions to optimize their visual function.
Comprehensive assessment parameters include:
- Visual acuity: Central and peripheral
- Visual fields: Central and peripheral
- Color vision
- Contrast sensitivity
- Ocular history and examination
- Medical history and medications
- Functional vision assessment
Techniques used to assess visual acuity and visual fields in clients with macular degeneration include:
- Snellen chart
- Amsler grid
- Goldmann visual fields
- Humphrey visual fields
Impact on Daily Activities

Macular degeneration significantly impacts a client’s ability to perform daily activities that rely on central vision, such as:
- Reading
- Driving
- Recognizing faces
- Cooking
- Navigating stairs
Challenges faced by clients with macular degeneration in different settings include:
- Home:Difficulty reading labels, cooking meals, and navigating stairs
- Work:Inability to perform tasks requiring detailed vision, such as computer work or reading documents
- Social situations:Difficulty recognizing faces, following conversations, and participating in social activities
Assistive devices and strategies can enhance independence and quality of life for clients with macular degeneration, such as:
- Magnifiers and telescopes
- Closed-circuit televisions (CCTVs)
- Audio books and talking clocks
- Visual aids (e.g., large-print books, talking calculators)
Nursing Interventions
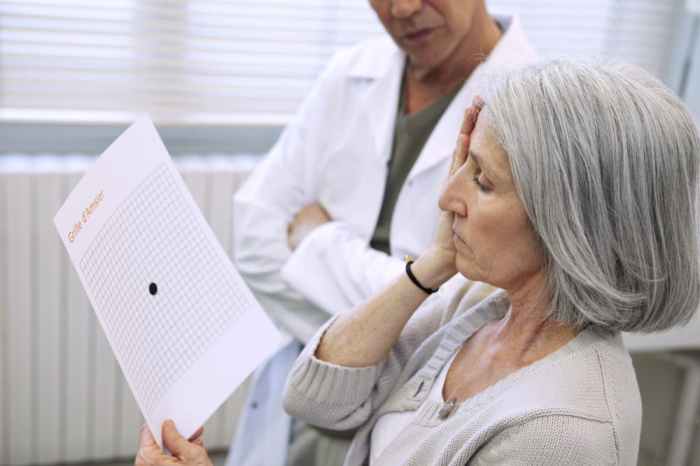

Nursing interventions for clients with macular degeneration aim to promote visual function and prevent further vision loss:
- Low vision aids:Prescribing and training clients on the use of low vision aids to enhance visual function
- Patient education and counseling:Providing information and support to clients about their condition, its impact, and available resources
- Monitoring and evaluation:Regularly assessing clients’ visual function and adjusting interventions as needed
- Collaboration with other healthcare professionals:Working closely with ophthalmologists, optometrists, and other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: A Nurse Is Assessing A Client Who Has Macular Degeneration
Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential for providing comprehensive care for clients with macular degeneration:
- Ophthalmologists:Diagnose and treat macular degeneration, perform surgeries, and prescribe medications
- Optometrists:Prescribe and fit low vision aids, provide vision rehabilitation, and monitor visual function
- Other healthcare professionals:Occupational therapists, physical therapists, and social workers address functional limitations, mobility issues, and social support
A team-based approach ensures that clients’ physical, psychological, and social needs are met, leading to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Essential FAQs
What are the early signs and symptoms of macular degeneration?
Early signs may include blurred vision, difficulty reading, and distorted images. As the condition progresses, clients may experience blind spots in their central vision and difficulty recognizing faces.
How is macular degeneration diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive eye exam, including visual acuity testing, visual field testing, and retinal imaging.
What are the treatment options for macular degeneration?
Treatment options vary depending on the type and stage of macular degeneration. They may include medications, laser therapy, and surgery.
How can nurses support clients with macular degeneration?
Nurses play a vital role in assessing, educating, and supporting clients with macular degeneration. They provide low vision aids, assist with daily activities, and collaborate with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care.